#Computer-Science#CS251#RuntimeAnalysis
Efficiency
- Tractability means having efficient computational solutions
- What does “efficient” mean in this sense?
- Originally it meant a solution that runs fast on a machine. However, what machine?
- Then it changed to meaning better performance than the brute force solution for the worst case
- Now an algorithm is considered efficient if it runs in polynomial time (this is the definition of efficiency we use)
Big O
- O(n) represents the asymptotic upper bound
- Definition: Given functions f(n) and g(n) then if there exists constants and where for all
- In other words, if doesn’t grow faster than
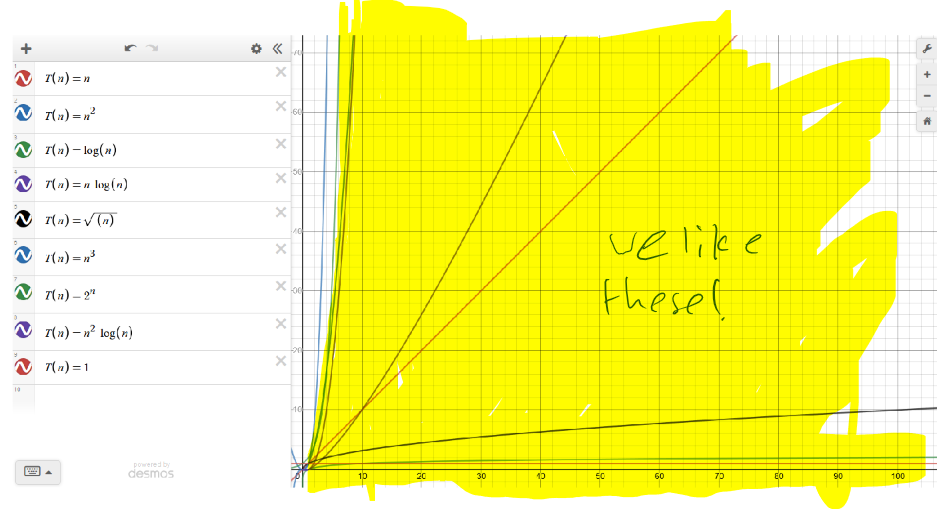
- Growth order of common functions:
- From the definition above, multiple functions can be big-O of another function
- For example, and
- Generally we want to give the tightest upper bound of a function.
- For example, if we have the function we don’t want to say even though it’s true. We would rather say since it’s the tightest upper bound
- When giving the of a function, you take the fastest-growing term and remove the constants from it
- Ex:
- Big O does not indicate the worst case of a function
Big Ω
- represents the asymptotic lower bound
- Definition: Given functions f(n) and g(n), then if there exists constants and where for all
- In other words, if doesn’t grow slower than
- Like how multiple functions can be O(n) of a function, multiple functions can be of a function
- For example, and
- Again, give tightest bound usually
- Process for getting big- of a function is the same as getting big-O
- Big does not indicate the best case of a function
Big θ
- represents the asymptotic tightest bound of a function
- if doesn’t grow faster or slower than
- Basically, should be BOTH and
- To prove something is you must prove that it is both and