#Computer-Science#Information
Binary §
- A number system that uses Base 2 compared to the normal decimal system that uses Base 10
- The only possible values are 0 and 1, so all numbers are comprised of a bunch of 0’s and 1’s
- A number in binary of length k and can represent 2k−1 values
- Each digit going from right to left is 2 to the power of the digits position. If there’s a one in that spot, add that to your decimal number, otherwise go to the next.
- Here’s a better example.
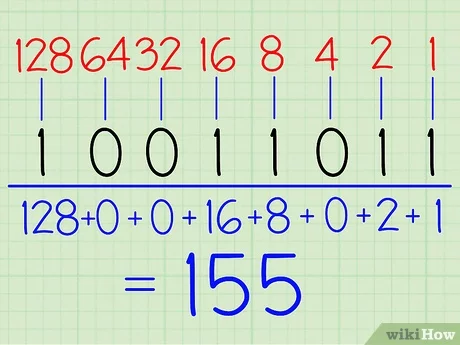
- Binary is used very commonly in computer science, so it is important to know
- A common representation of binary numbers starts with 0bNUMBER
- The number above would be, 0b10011011
Hexadecimal §
- To aid in expressing binary values, we use Hexadecimal
- Hexadecimal is very similar to binary, except it uses base 16 instead of base 2.
- The values for Hex are - 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F
- Hex offers two main advantages
- More compact than binary, allowing for shorter representations
- Since sixteen is a power of two, conversion between binary and hex is fairly easy
- Hex basically groups each group of four bits as a single hex digit
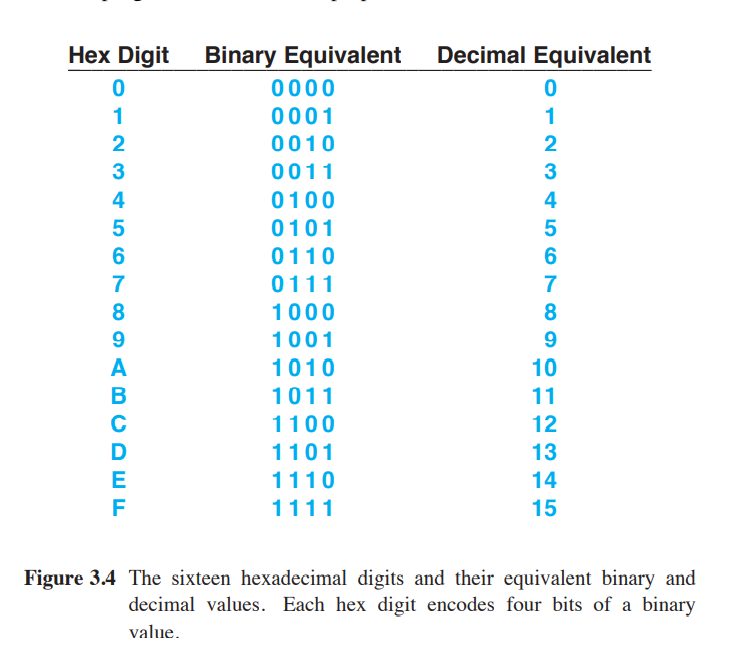
- Example of hexadecimal encoding, converting binary string to hexadecimal
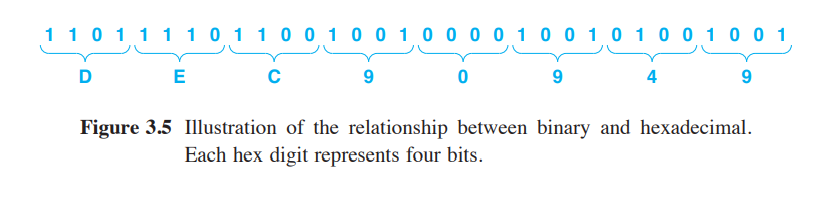
- Hexadecimal numbers are most often written as 0xNUMBER to denote that the number is in Hex and not anything else.
- As an example, the number from figure 3.5 above is written as 0xDEC90949


