- Early (Hadean) Earth was inhospitable
- Basically just a ball of magma
- Meteors bombarded Earth’s surface
- Accretion from planetisimals
- Elevated rate of impacts copmared to today
- Partially molten
- Differentiated core/mantle/early crust
- Moon forming impact (about 4.5-4.4 billion years ago)
- Impact from a Mars-sized body ejected material that coalesced into the moon
- “Late heavy bombardment”
- 4.1-3.8 billion years ago
- Increased rate of impacts
- Delayed origin of life? Multiple origins of life?
- Extensive volcanism
- Considerable heat from
- Formation/impacts
- Radioactive decay
- Volcanic gases formed atmosphere
- Continental “rocks” in the Hadean
- Initially no continents
- No intact crustal rocks known prior to 4.28 billion years ago
- Archean sedimentary rocks, Western Australia (Jack Hills)
- One zircon with age 4.4 billion years ago, the oldest material found on Earth
- Earliest evidence of continental crust and oceans on Earth
- Oxygen isotope ratios indicate interaction with liquid water
- Precambrian rock distributions
- Shields (areas of exposed precambrian rocks)
- Platforms (areas of buried precambrian rocks)
- Craton (Shield + adjoining platform)
- Cratons are stable continental cores
- Present on all continents
- Subsequent deformation at edges
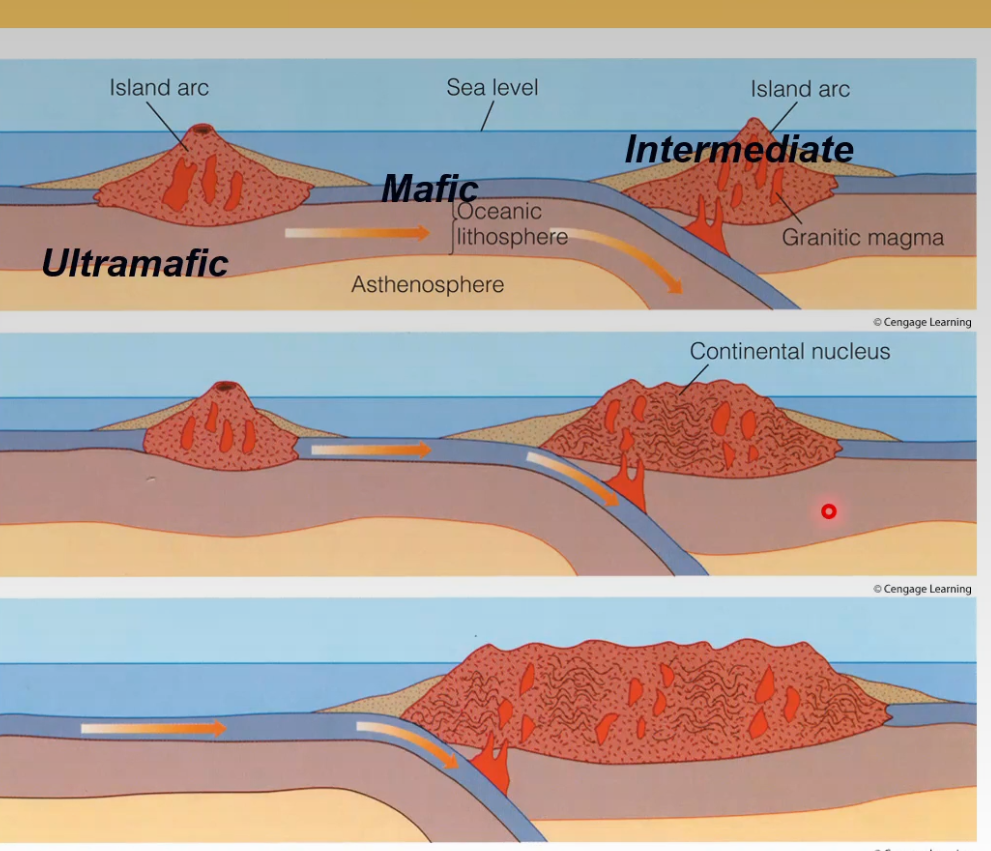
- Modern continental crust formation
- Oceanic lithosphere subducts
- Partial melting of mafic oceanic crust (bassalt/gabbro)
- Intermediate composition melt (andesite/diorite) -> island arcs
- Partial melting of andesite
- Felsic composition melt (rhyolite/granite)
- The continental crust is intermediate in composition and less dense than the oceanic crust
- Ocean basin between two island arcs would close by subduction
- Island arcs collide
- Forms continental core
- Process repeats