Rocks §
- A rock is a naturally formed consolidated material composed of grains of one or more minerals
- Earth’s surface is extremely diverse in terms of rock makeup and types etc
- Made up of one or more minerals/pieces of other rocks
- They form through different geologic processes
- Three types of rocks, Igneous, Sedimentary, Metamorphic, all defined by the process that creates them
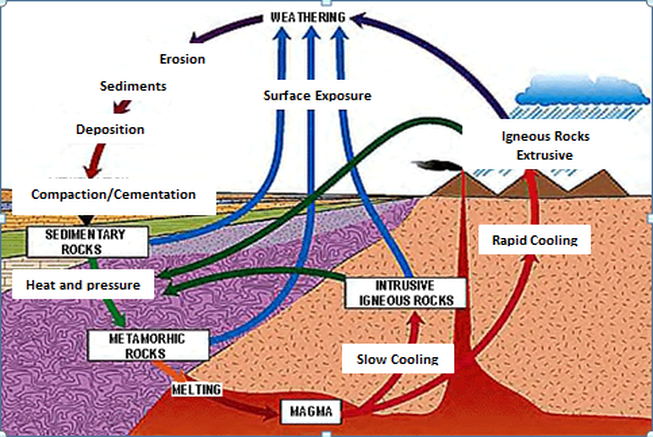
- The rock cycle shows how rocks are created and destroyed
- Plate tectonics play an important role in the rock cycle
- Sediments are transported, buried and lithified, forming sedimentary rocks
- Sedimentary and igneous rocks are altered forming metamorphic rocks
- Earth’s internal heat and pressure melts material, producing igneous rocks
- Plate Tectonics and the rock cycle
- Uplift (surface exposure) happens due to tectonics. Mostly happens at convergent boundaries
- Space for sediments is often created by tectonic motions, at divergent boundaries
- Metamorphism often occurs at convergent boundaries. It can alter any type of rock
Minerals §
- minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic, crystalline solids
- they have specific chemical composition and distinctive physical properties
- Rocks are composed of one or more minerals
- Minerals have 5 characteristics
- Solid
- Naturally ocurring
- Inorganic
- Ordered internal structure (crystalline)
- Orderly arrangement of atoms in a repeating pattern
- The internal structure influences the external form
- Specific chemical composition
- About 4,000 minerals have been found so far
- Major mineral groups
- Silicates (SiO)
- Make up most of our crust so very important
- These minerals are made up of Silica Tetrahedra. A silica atom surrounded by four Oxygen atoms
- Carbonates (CaCO)
- Halides (F, Br, Cl, I)
- Oxides (O + metal)
- Sulfides (S + metal)
- Sulfates (S + O)
- Native minerals (single elements)
- Key Minerals are Quartz and Feldspar (both abundant at the surface) and Olivine and Pyroxene (both abundant in mantle)
Atoms, Elements, and Isotopes §
- Chemical elements make up matter
- Atoms: nucleus (protons and neutrons) and electrons
- Atomic Number
- Number of protons (= # of electrons)
- Atomic mass number
- Number of protons + neutrons
- Isotopes
- Same element, different numbers of neutrons
- Some isotopes are stable, some are unstable
- Some unstable ones decay to a more stable one
- Making a mineral involves the bonding of atoms
- The type of bonding can affect a minerals strength and qualities (e.g. covalent vs ionic bonds)
