- Plate movement over time has resulted in the features we see on Earth
- Configuration of continents and oceans has driven changes in live on Earth
- James Hutton - Principle of Uniformitarainism
- “The present is the key to the past”
- A fundamental principle of geology
- Modern Earth processes also occurred in the past over logn periods of time
- Very gradual and slow events
- Very rapid and catastrophic events
- Everything in between
- Recognition of gaps in the rock record (unconformities)
- Lord Kelvin
- Earths history is NOT short
- Tree rings have bands extending back 10,000 yaers
- Seasonal bands of fine sediments, thick sequences up to millions of years
- Current rates of plate motion, those basins must have taken over 100 million years to form
- Where age of Earth comes from
- We get the age of Earth from meteorites, which are roughly 4.55 billion years old
- We also have dated moon rocks, at 4.5 billion years
- The oldest dated Earth rocks are 4.4 billion years ago
- We also use data from astronomy on the age of the solar system and universe
- Geologic Deep Time
- Immense time spans
- If age of Earth was compressed into 1 year, humans would appera at 11:36 PM on December 31
- Importance of studying geologic time
- Place mdoern environmental processes in long term context
- Privdes a framework fo rinteprreting past goelogic events
- Aldo fundamental to physical and biological scineces
Geologic Time Scale §
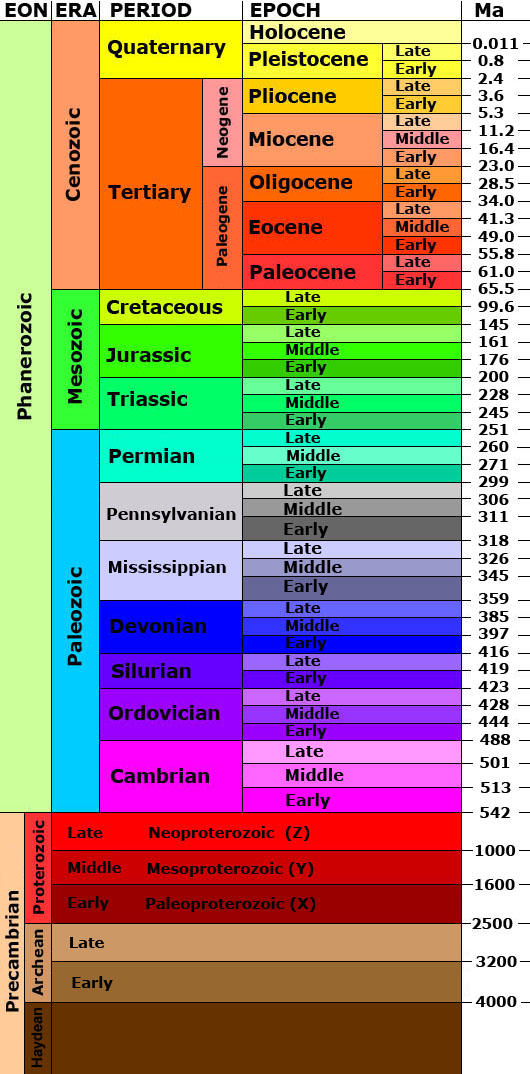
- Time units designate specific intervals of geologic time
- Divided into
- Era: two or more periods
- Eon: two or more eras
- Periods divided into epochs
- Geologist think we should be in a new epoch entirely, we should be in “Anthropocene” epoch rather than Holocene, since humans have had such an impact on Earth
- Look closely at the years on the right of the timeline above, You can see that the Phanerozoic takes place closer to the end, and that’s where most evolution happened
Dating Rocks §
- Relative Dating
- Understand what happened in which order
- Specific age not necessary
- Numerical dating
- Determine the numerical age of an event or rock using laboratory methods
- Correlation
- Connect the pieces of the geologic record together
- Construct a coherent and complete history for all areas of the planet
Relative Dating §
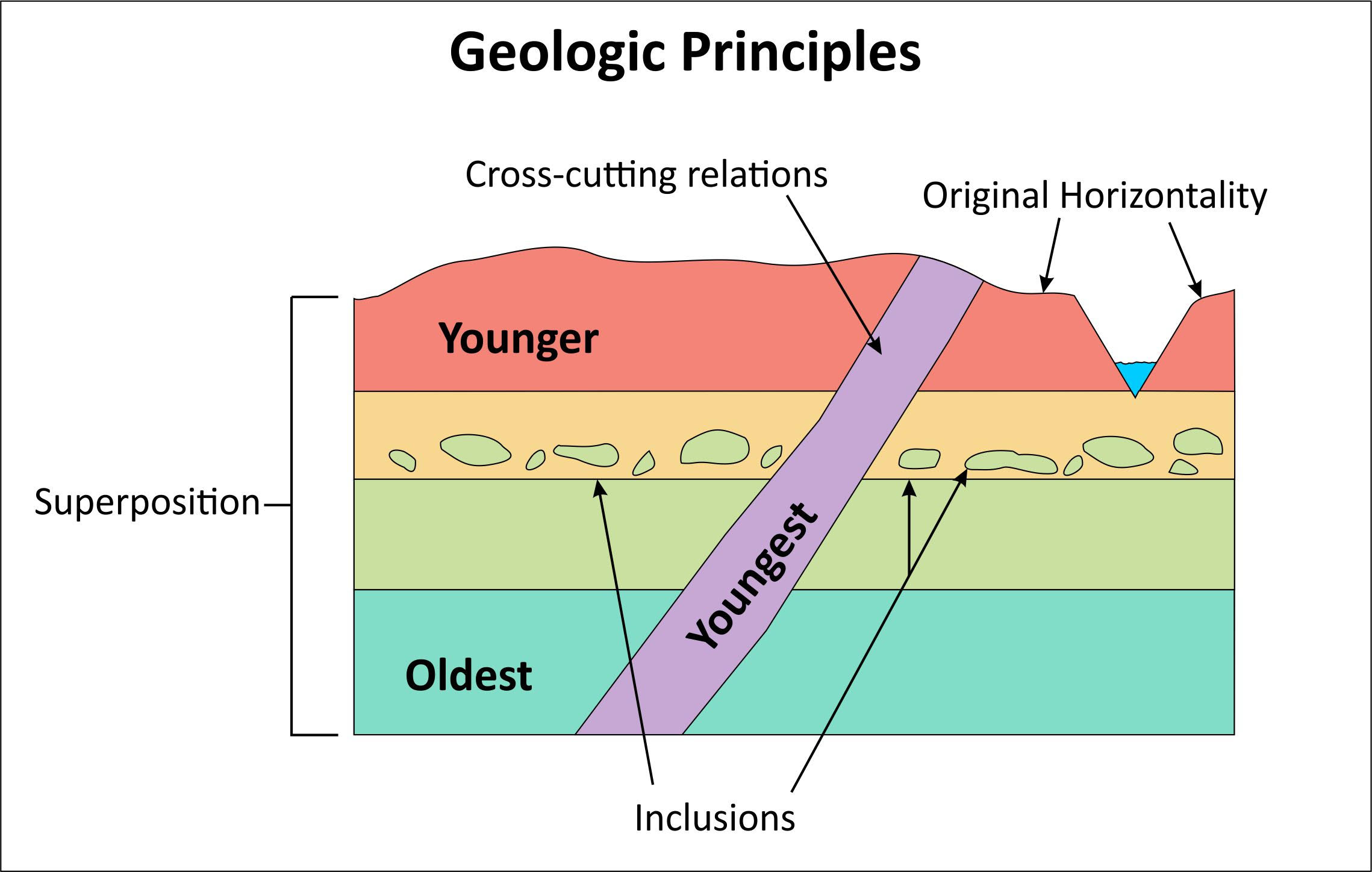
- Superposition
- Older rocks are on the bottom, younger rocks are deposited on top
- Only applies for sedimentary and volcanic rocks
- Watch out for the effects of extreme deformation like tilting
- Original horizontality
- Sedimentary rocks are originally horizontal and flat lying
- Lateral continuity
- Sediments extend laterally in all directions
- Until thins and pinches out OR ends up against the edge of a depositional basin
- Cross-cutting relationships and inclusions
- Any rock body cross-cut by a fault, intrusion or other event must be older
- Rocks included as clasts in units above them, they must be older than the rocks containing them