Paleozoic Paleogeography §
- Data for paleogeographic reconstructions
- Paleomagnetism
- Declination (D)
- Angle between magnetic north and geographic north
- Inclination (I)
- Angle between magnetic field direction and the horizontal
- Directions frozen in igneous rocks
- Paleoclimate
- Fossils
- Stratigraphy
- Sedimentology
- Tectonics
Early Paleozoic Earth §
- Includes Cambrian, Ordovician, and Silurian periods (541-419 million years ago)
- Several orogenic episodes occurred
- Taconic orogeny on eastern margin of Laurentia
- Widespread sedimentary deposition
- Sauk and Tippecanoe sequences (sets of sedimentary dpeosits)
- Development of thick strata in basins
- Evidence of sea level changes related to plate tectonics and glaciation
- Explosion of life
- Contintental Architecture
- Supercontinent Pannotia
- Starts to break up ~550 million years ago
- Early Paleozoic has six major continents
- Baltica: Western Russia and most of Northern Europe
- China: China, Indochina, Malaysia
- Gondwana, Africa, Australia, Antarctica, Florida, India, Madagascar, Middle East, Southern Europe
- Kazakhstania: Centered on Kazakhstan
- Laurentia: NOrth America, Greenland, NEW Ireland, Scotland
- Siberia: Russia east of Urals, Asia between Kazakhstan and Mongolia
- Each continent had two major parts
- Stable craton and platforms
- Epeiric (aka epicontinental) seas
- Shallow inland sea over craton
- Transgressions and regressions
- Mobile belts
- Elongate collisional tectonic zones
- Margins of cratons
- Sites of subduction and mountain building
- North America in the Paleozoic
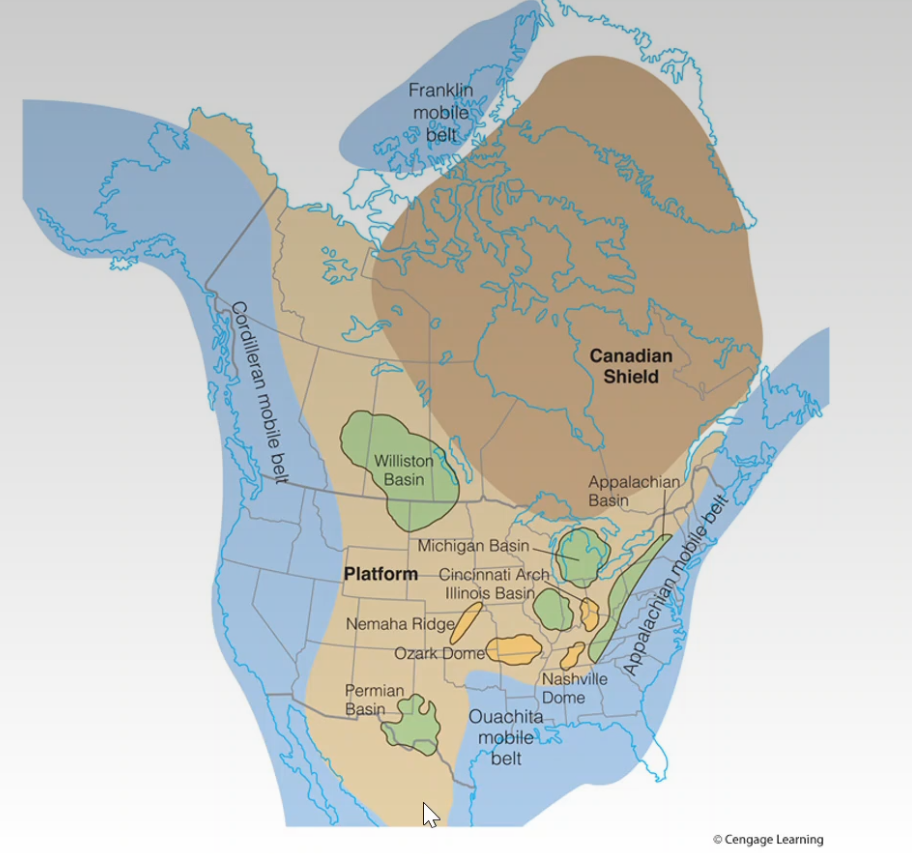
- Four major mobile belts
- Appalachian
- Ouachita
- Cordilleran
- Franklin
- Major cratonic structures
- Shield
- Platform
- Domes - circular structure with uplifted center
- Basins - circular structure with depressed center
- Michigan Basin
- Illinois Basin
- Appalachian Basin
- Arches and ridges - broad, structural uplifts
Paleozoic Paleogeography §
- Less well known than Mesozoic and Cenozoic
- No seafloor magnetic anomalies
- Destroyed by subduction during the formation of Pangaea supercontinent
- Primarily based on
- Structural relationships
- Climate-sensitive sedimentary rocks
- Red beds, evaporites, tillites, and coals
- Fossil distributions
- Late Cambrian Paleogeography
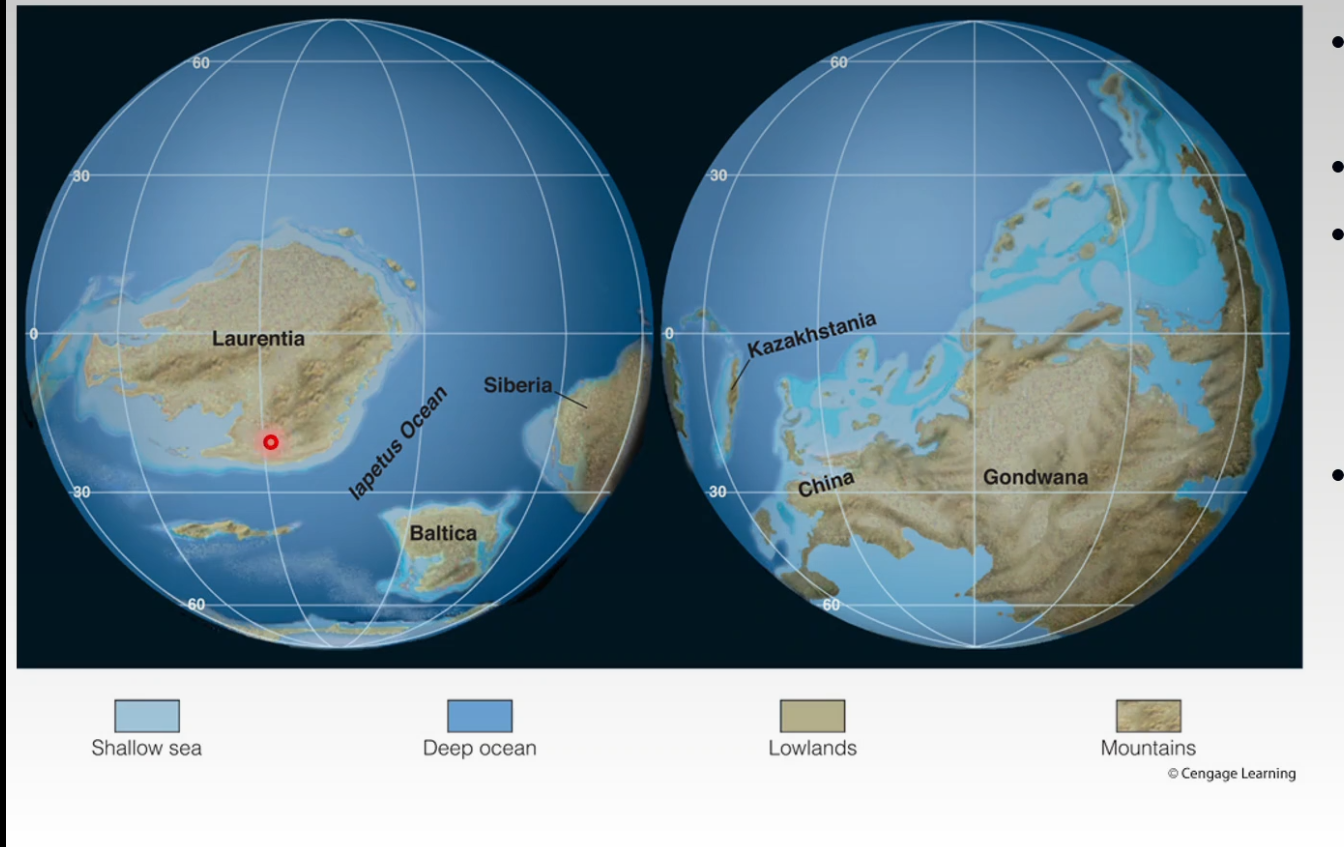
- Polar regions were mostly ice free
- Epeiric seas
- Highlands
- Gondwana
- Siberia
- Kazakhstania
- Eastern Laurentia had a passive margin where sediment accumulated
- Late Ordovician Paleogeography
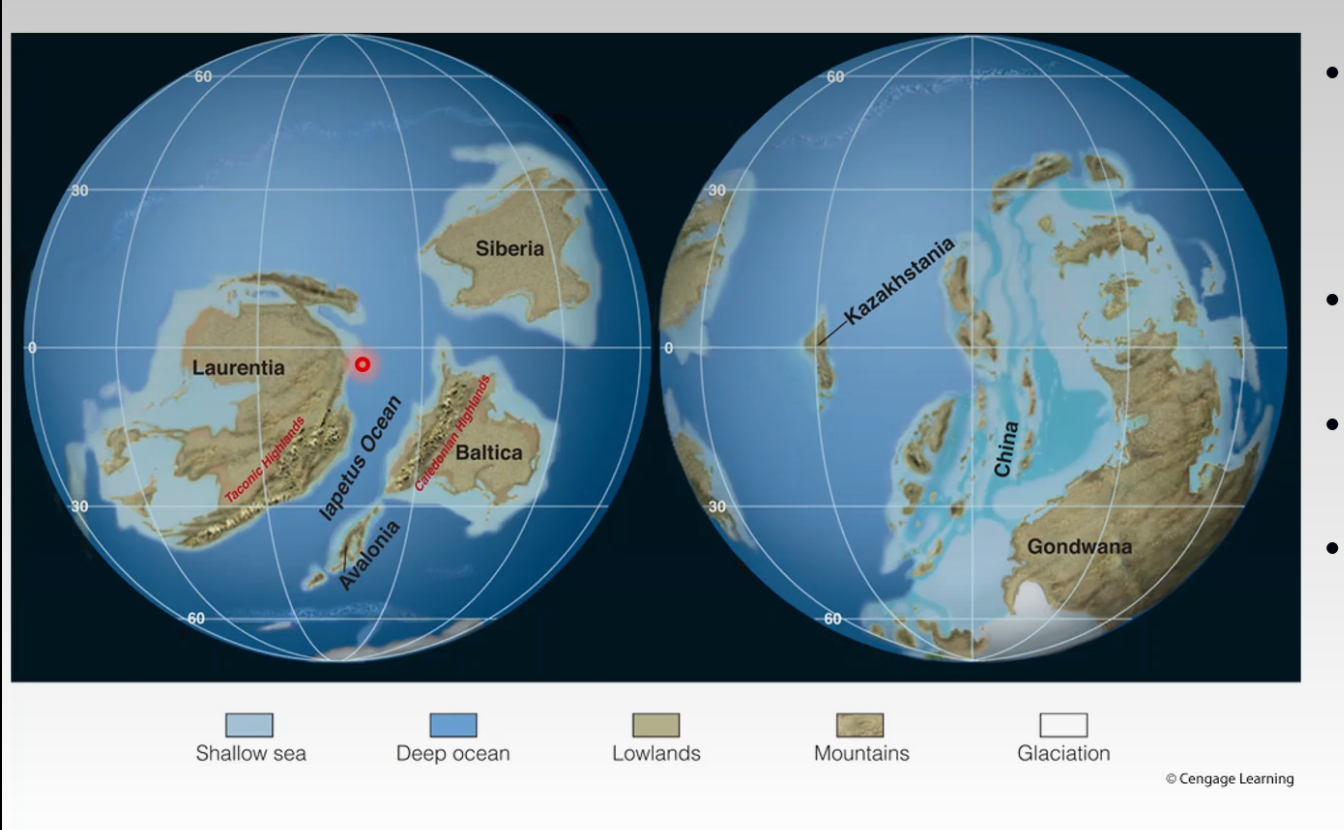
- Gondwana moved southward and corssed the South Pole
- Glaciations caused Tillites in North Africa
- Avalonia collided with Baltica
- Subduction of iapetus ocean beneath Eastern margin of Laurentia
- Middle Silurian Paleogeography
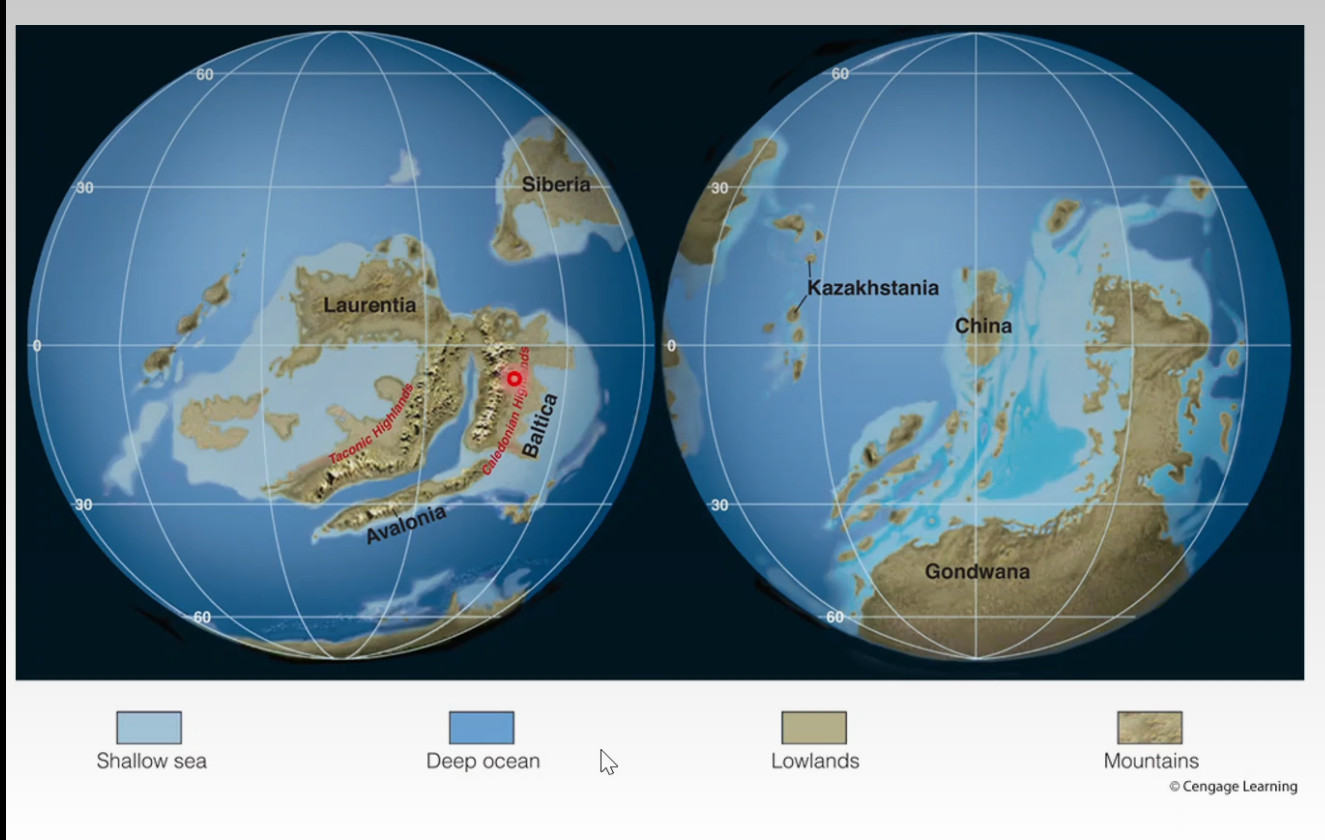
- Baltica-Avalonia collided with Laurentia -> Laurasia
- Caledonian orogeny
- Closed the northern iapetus ocean
- Southern iapetus ocean remained open
- Siberia and Kazakhstania moved to a northern temperate latitude



