- Crystallize from a melt of some kind
- Magma is molten rock underground
- Lava is molten rock at the surface
- Intrusive igneous rocks cool slowly underground for 1000s to millions of years
- Extrusive igneous rocks reach the surface and cool very quickly, seconds to 1000s of years
- We classify igneous rocks often based on texture and composition
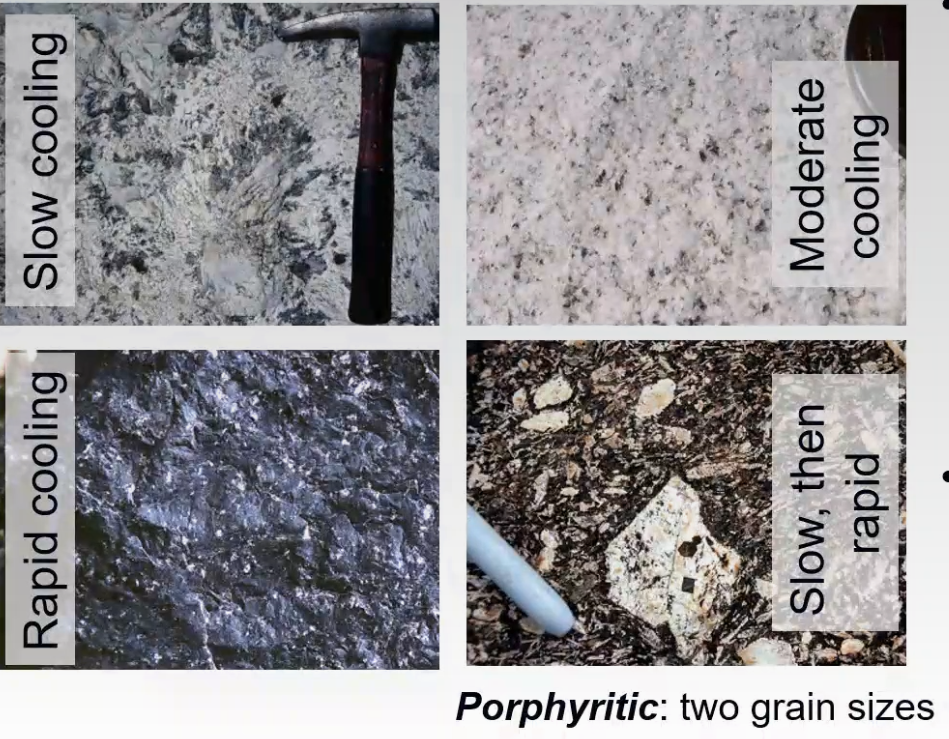
- Texture
- Sizes of the individual mineral grains depend on the cooling rate of the magma
- Phaneritic: coarse-grained, formed by slow cooling
- Aphanitic: fine-grained, formed by rapid cooling

- Composition
- What elements are present in the magma?
- Directly affects which minerals form when the magma cools
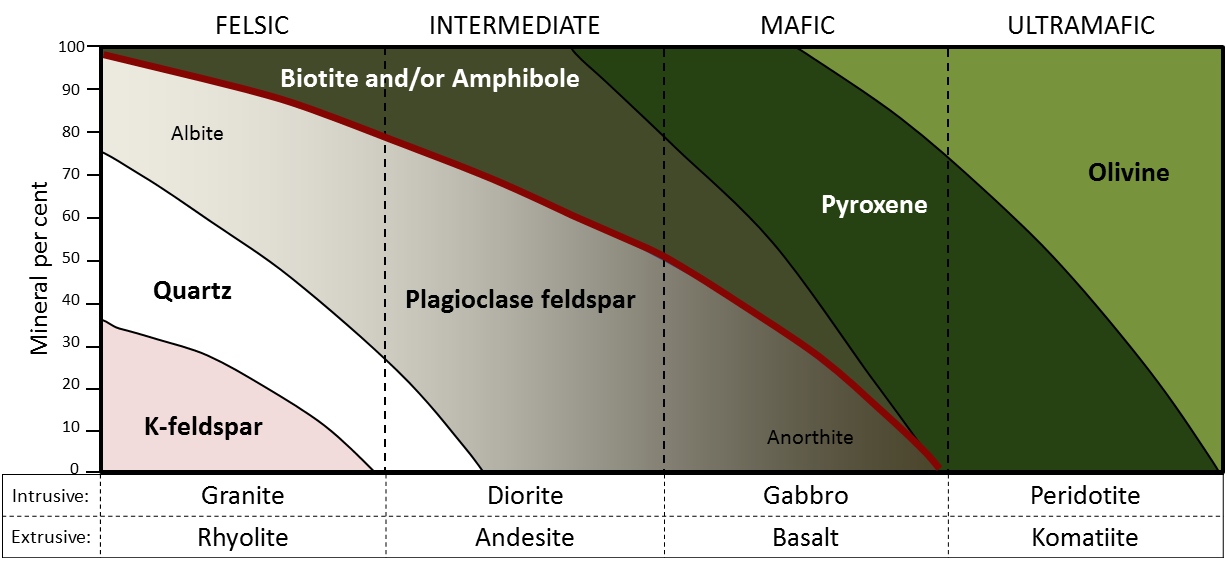
- Felsic means high silica content, Mafic means low silica content
- Bowen’s Reaction Series is responsible for different minerals forming in igneous rocks

