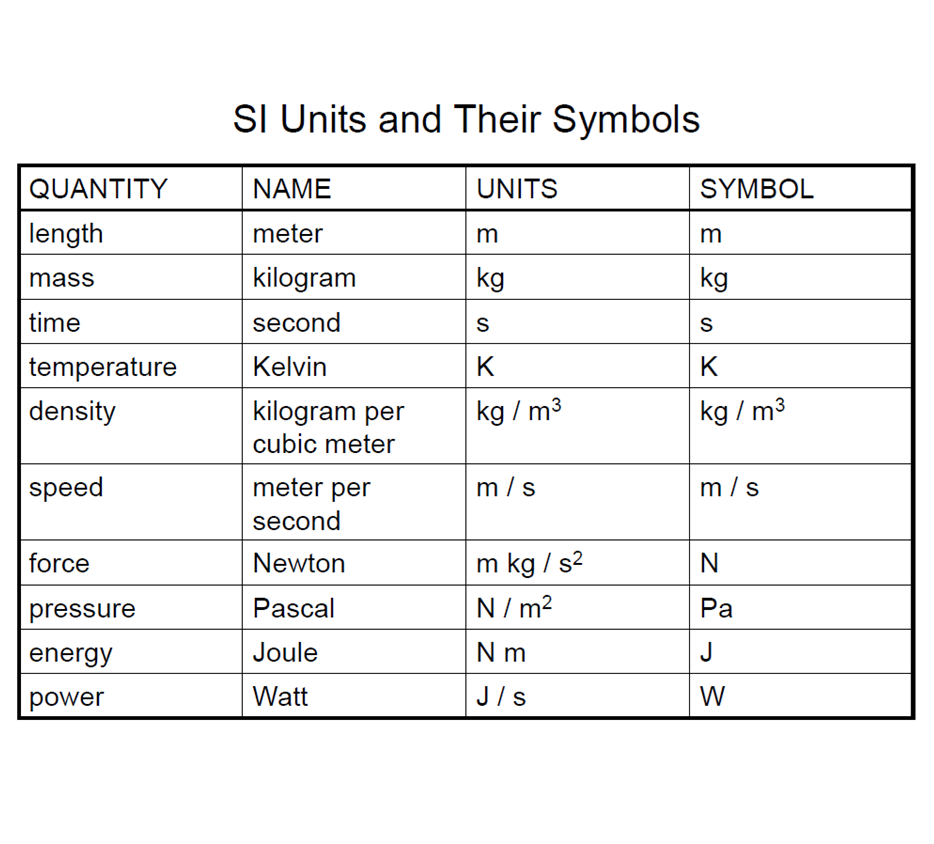
- To study the physical state of the atmosphere in space and time, a meteorologist is interested in measuring: pressure, temperature, water vapor, and wind. Given pressure and temperature one can compute density as well. Pressure, temperature, density, and water vapor are scalar quantities, while wind velocity is a vector quantity.
5 Key dependent meteorological variables
- Temperature (T) - measured with a thermometer - scalar
- Pressure (P) - measured with a barometer (scalar)
- Density () - calculated - scalar
- Relative Humidity (RH) - measured with a hygrometer or calculated - scalar
- Wind Velocity () - measured with an anemometer and wind vane - vector
The four independent variables
- X (West to East)
- Y (South to North)
- Z (up)
- t (time)
Pressure
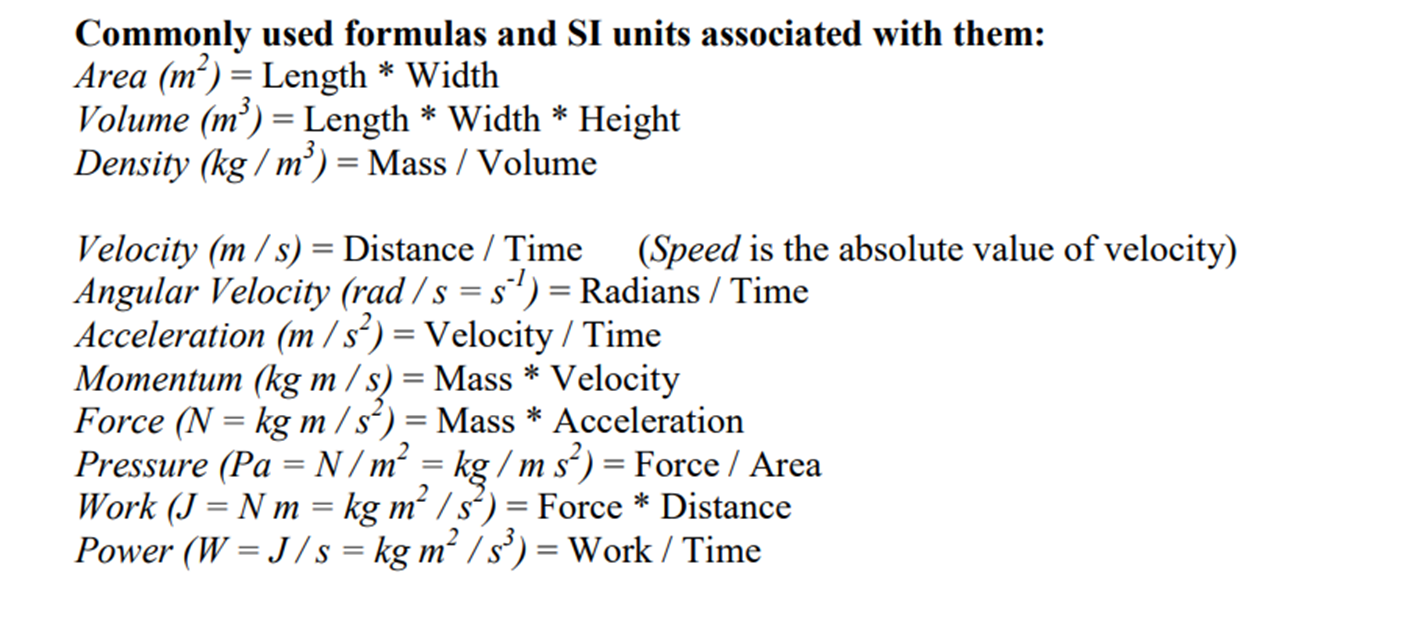
- Pressure is force over an area ()
- weight of atmosphere above an area
- units = = Pascals
- 1 Pascal = 1 Newton per square meter
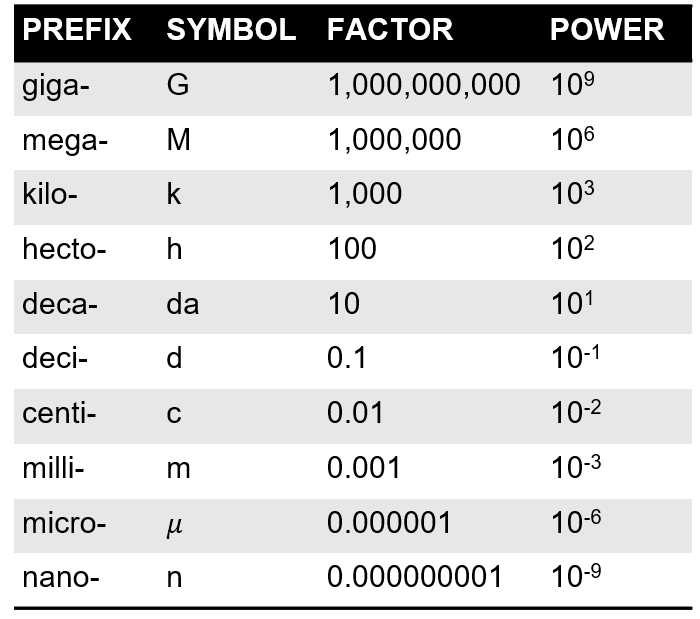
- 1 Hectopascal (hPa) = 1 millibar (mb)
- 1 millibar (mb) = 100 pascals (Pa)
- 1 standard atmosphere = 1013.25 mb = 760 mmHg = 29.92 in. Hg = 14.7 psi = 101325 Pa
- The FORCE that produces air pressure is simply the WEIGHT of the atmospheric column -> Weight = Mass x Gravitational Acceleration
Density
- Density is mass over volume ()
- units =
- pressure and density decrease with height due to gravity
- Used in Ideal Gas Law
Mass, Density, and Weight of an Air Parcel
- Mass is the quantity of matter in an air parcel
- The mass of an air parcel is equal to the sum of the masses of all the molecules of permanent and variable gases
- Density is mass per unit volume
- if matter is not allowed to leave or enter an air parcel, its MASS is conserved as it travels around but the DENSITY will change if its volume changes
- Weight is the gravitational force acting on the air parcel. Weight = mass x gravitational acceleration
Temperature
- Atmospheric temperature is a measure of the average speed (kinetic energy) of the atoms and molecules that make up a parcel of air
- Temperature at the surface in the US is reported in units of degrees Fahrenheit
- Temperature above the surface in the US as well as all international observations are reported in units of degrees Celsius
- When temperature represents energy it is stated in degrees Kelvin
- Absolute zero = 0 K. This is the point where all molecular motion stops
- Used in Ideal Gas Law
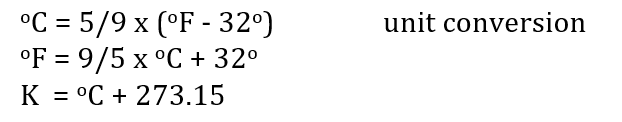
Lapse Rate
- Lapse rate is the rate at which temperature decreases with increasing height
- Usually denoted by Greek letter capital gamma ()
T represents temperature and Z represents altitude.
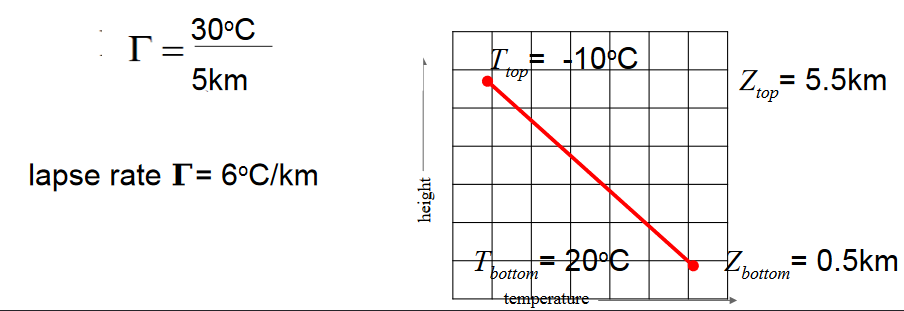 Example ^
Example ^ - An inversion layer is one in which the temperature INCREASES with INCREASING altitude, i.e.
- An isothermal layer is one in which the temperature does not change with increasing altitude, i.e.
- corresponds to a layer where temperature decreases with increasing altitude, which is the typical situation in the Troposphere
Humidity
- Humidity is a measure of water vapor content
- Specific humidity (q) = mass of water vapor per unit mass of moist air
- Relative humidity (RH) = mass of water vapor divided by the mass of water vapor required for saturation
- Dewpoint Temperature () = the temperature at which air becomes saturated when cooled at constant pressure
Wind
- Wind is the motion of air relative to the Earth’s surface
- Speed of wind is the distance traveled per unit time
- Direction of wind is the orientation of the travel path (taken as direction from)
- It’s a Vector
Time
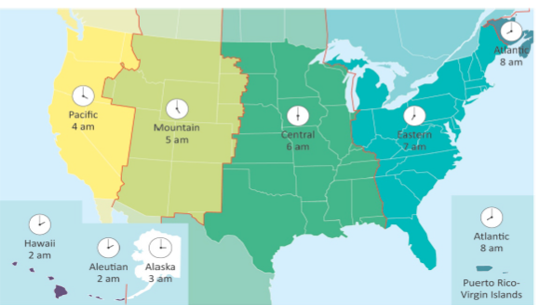
Because we need to measure the global state of the atmosphere at the same time, by convention we use the local time (the Sun is at its highest point in the sky at local noon) at the prime meridian (0 degrees longitude) this is referred to as
- UTC (Universal Time Coordinated)
- GMT (Greenwich Mean Time)
- Z (Zulu)
and is expressed in XXYY where XX is hours after midnight in a 24 hour clock and YY is minutes. Since the Earth rotates through 360 degrees of longitude in 24 hours, local time changes by 1 hour for every 15 degrees of longitude.
Standard time is an administrative regulation designed to ease commerce. Easter Standard Time (GMT - 5 hours) is equal to the local time at 75 degrees West longitude (in Philadelphia, PA)
West Lafayette is at 86 degrees West and the Sun is at its highest point around 12:44 PM EST