Proterozoic Eon §
- 2.5 billion years ago to 541 million years ago (42.5% of geologic time)
- Proterozoic rocks
- Many more rocks exposed than Archean
- Ultramafic mantle-derived volcanic rocks became rare
- Appearence of shallow marine strata
- Banded iron formations
- Growth of (super)continents
- ~43% of modern continental crust came from this time period
- Proterozoic events
- Great Oxidation Event
- Snowball Earth glaciation (at least 3x)
- Boring billion (1.8-0.8 billion years ago)
- Ediacaran Fauna
- Proterozoic Supercontinents
- Columbia/Nuna
- 1.6 billion years ago
- Created by collisions and suturing of Archean proto-continents
- Made up of proto-cratons that make up cores of most modern continents
- Rodinia
- 900 million years ago
- Mostly located along equator
- Began to fragment 750 million years ago
- Pannotia
- 600 million years ago
- Short-lived (existence is debated)
- Centered on south pole
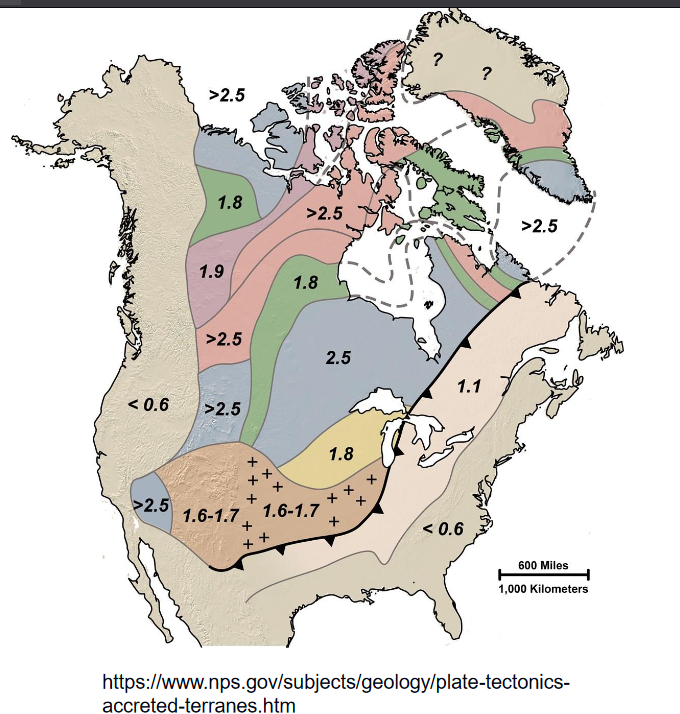
- Poterozoic History - Laurentia
- Basement rock = craton
- Crystalline igneous or metamorphic rocks that lie beneath sedimentary rock
- Can be any age, but most is Archean and Proterozoic
- Orogeny
- Mountain-building events
- Deformation, igneous intrusions
- Laurentia
- Craton of North America and Greenland
- Major continent of Proterozoic
- Lon, complex history of orogenic events and sutering
- Wilson Cycle: Stages of evolution of continents and oceans
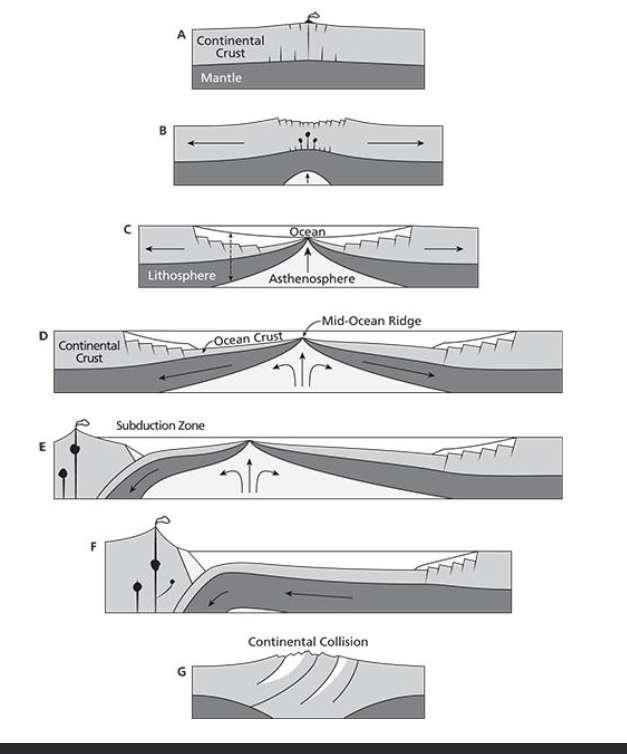
- (A and B) Continental stretching and rifting
- (C) seafloor spreading begins, forming a new ocean basin
- (D) the ocean widens and is flanked by sedimented passive margins
- (E) subduction of oceanic lithosphere begins on one of the passive margins
- (F) so the ocean basin gets smaller
- Eventually, the ocean basin is all subducted away and the continents collide, building a mountain range (G)
- This helps to explain the evolution of Laurentia
- The Great Oxidation Event
- ~2.3-2.0 billion years ago, rise in atmospheric oxygen and ocean sulfate
- Result of cyanobacteria producing oxygen through photosynthesis
- Important implications for life evolution (free oxygen, ozone to block UV radiation, respiration)
- Evidenced by BIFs, red beds, fossils, isotopic evidence
- Snowball Earth
- Rises in Oxygen -> reductions in CH4?
- Clustering of continents at low latitudes
- Allows extensive weathering and CO2 drawdown?
- Accumulating snow and ice
- Increases Earth’s albedo (reflectance) leading to further cooling and ice accumulation
- Two main Neoproterozoic glaciatiations
- Sturtian (720-660 million years ago)
- Marinoan (650-630 million years ago)
- Ending of Snowball Earth
- Volcanic and metamorphic CO2 emissions accumulate in atmosphere
Proterozoic Life §
- Stromatolites
- Increase in size of continents made more continental shelf available
- Greatest diversity 1.2 billion years ago
- Early eukaryotes
- Unicellular organisms - Acritarchs and others
- Algae - cyanobacteria became major producers in marine environments after 2 billion years ago
- Beginnings of animal life
- Neoproterozoic evolutionary radiation
- Evidence of multicellular life as much as 780 million years ago in trace fossils
- 650-600 million years ago have sponge body fossils and soft-bodied bilaterally symmetrical organisms

- The Ediacaran Environment
- 635-539 million years ago (end of Proterozoic)
- coincides with rapid retreat of ice sheets and glaciers
- Some of first evidence of multicellular life
- Likely fed on dissolved organic material on seafloor
- Microbial mats - sediment + colonies of microbes
- Evidence of high salinity, low surface productivity oceans with increasing oxygen levels
- Ediacaran Fauna
- Originally identified in Ediacara Hills, Australia
- Latest Neoprotroerozic
- 570-541 million years ago
- No hard parts
- Uncommon fossils
- Just impressions (trace and body)
- Found on 6 of 7 continents
- Three phyla may be present
- Cnidaria - jellyfish and sea pens
- Annelida - segmented worms
- Arthropoda - jointed legs
- Possible early echinoderms
- Burrowing
- After 600 million years ago, clear evidence of burrowing disrupts layered sediments
- mm-scale, simple, mostly horizontal/parallel and near sediment surfaces
- segmented worms?
- Skeletal fossils?
- nested cone structures made of calcium carbonate (Cloudina)
- Spicules and fossizlied sponges


